Importing Datasets
Colab Link
Key Concepts
- Understand the Data
- Importing and Exporting Data with Python
- Getting Started Analyzing Data with Python
- Python Packages for Data Science
Understanding the Data
Importing Datasets
Data is usually stored in plain formats that facilitate teh delivery and use of it. With python libraries like pandas the call and processing to a dataframe is eased while having a convenient way of manipulating the data like matrices and tensors in a fluid fashion with the flexible embedded functions.
Some basic/useful commands:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("path_to_datafile") #can swap the "_csv" with _json, _excel, _hdf, _sql
df.describe(include = "all") # Returns a dataframe with basic statistics from the dataset columns like count, mean, std, min, max and quartiles
df.[['col1','col2']].describe()
df.info() # Provides a concise summary of the dataframe
df.head(n) # shows "n" first values
df.tail(n) # shows "n" last values
df.columns = headers # Strings arrays with names, ej. headers = [col1, col2, col3, col4, coln]
df.dropna(subset = ["col_name"], axis = 0)
df.to_csv("path_to_file_export") # exports dataframe to csv, can also swap to other data formats
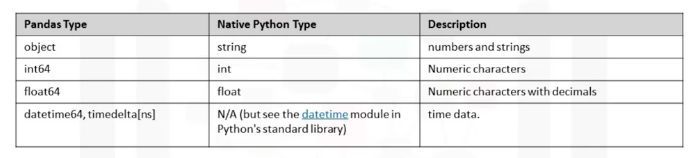
df.dtypes # shows dataframe data types
Python Packages for Data Science
- Scientific Computing:
- Pandas (Data structures and tools)
- NumPy (Arrays and Matrices)
- SciPy (Integrals, solving differential equations, optimization)
- Visulization:
- Matplotlib (Plots and Graphs)
- Seaborn (Plots, avanced (?))
- Algorithmic:
- Scikit-learn (Machine Learning, regression, classification)
- Statsmodels
Basic Data Types
Connecting to Databases
Python can connect to databases and extract data using SQL API's. Basic functionality is shown:
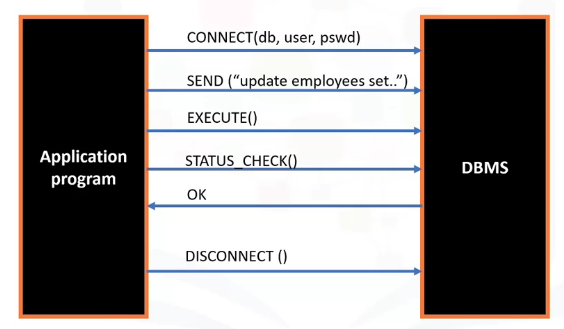
A basic code template is like:
from dbmodule import connect
# Create connection object
connection = connect('database_name','username','password')
# Create a cursor object
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Run queries
cursor.execute('select * from table')
results = cursor.fetchall()
# Free resources
cursor.close()
connection.close()